|
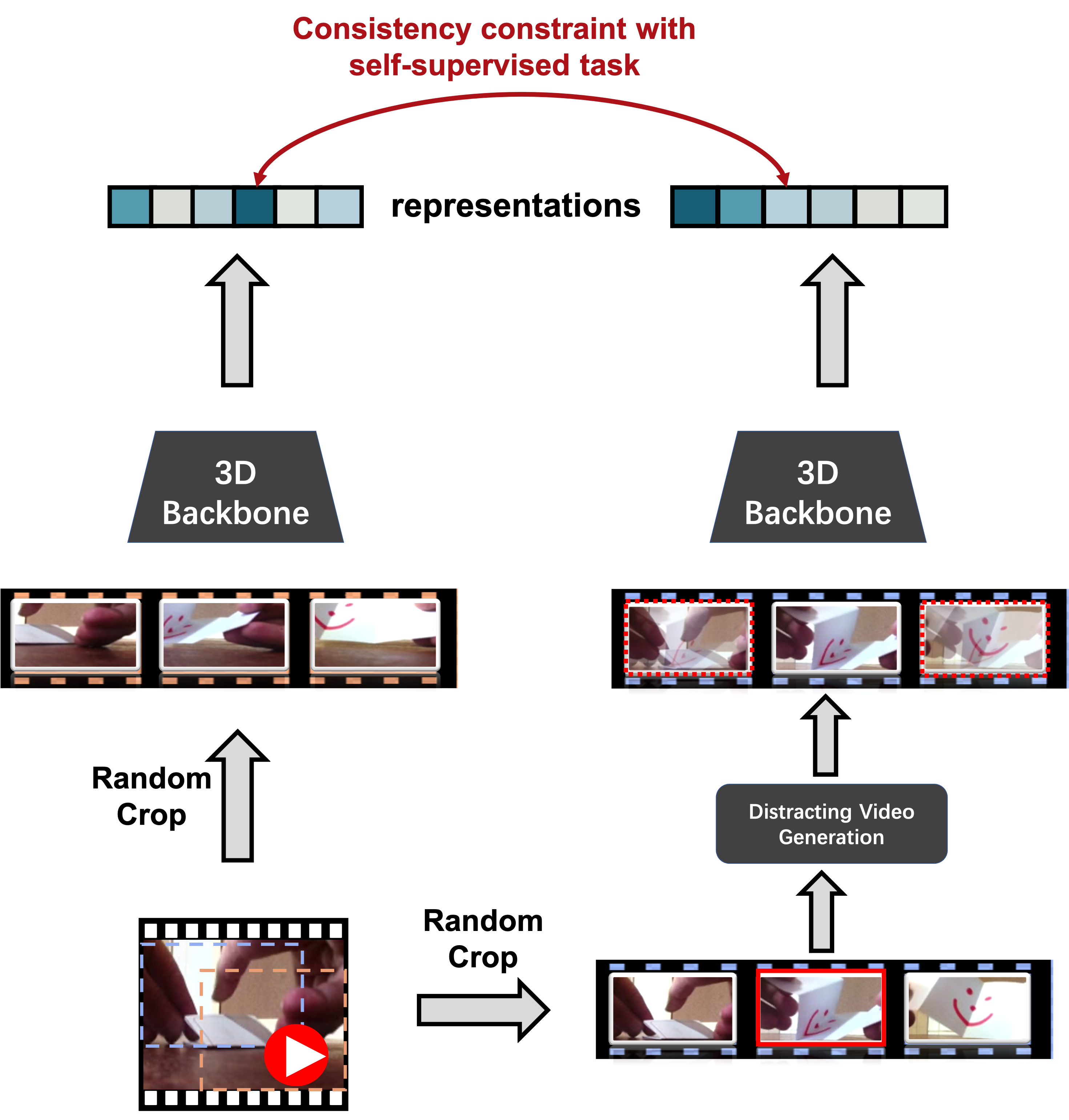
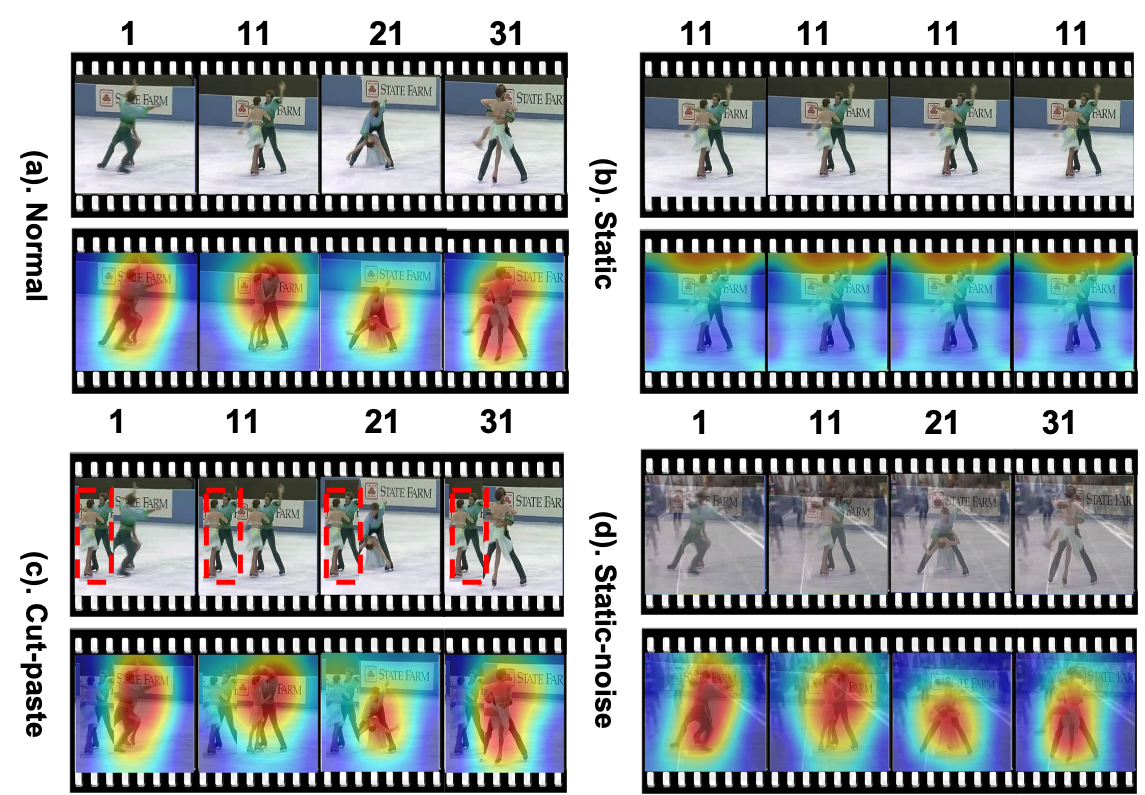
Self-supervised learning has shown great potentials in improving the video representation ability of deep neural networks by getting supervision from the data itself. How- ever, some of the current methods tend to cheat from the background, i.e., the prediction is highly dependent on the video background instead of the motion, making the model vulnerable to background changes. To mitigate the model reliance towards the background, we propose to remove the background impact by adding the background. That is, given a video, we randomly select a static frame and add it to every other frames to construct a distracting video sam- ple. Then we force the model to pull the feature of the dis- tracting video and the feature of the original video closer, so that the model is explicitly restricted to resist the back- ground influence, focusing more on the motion changes. We term our method as Background Erasing (BE). It is worth noting that the implementation of our method is so sim- ple and neat and can be added to most of the SOTA meth- ods without much efforts. Specifically, BE brings 16.4% and 19.1% improvements with MoCo on the severely biased datasets UCF101 and HMDB51, and 14.5% improvement on the less biased dataset Diving48.
|